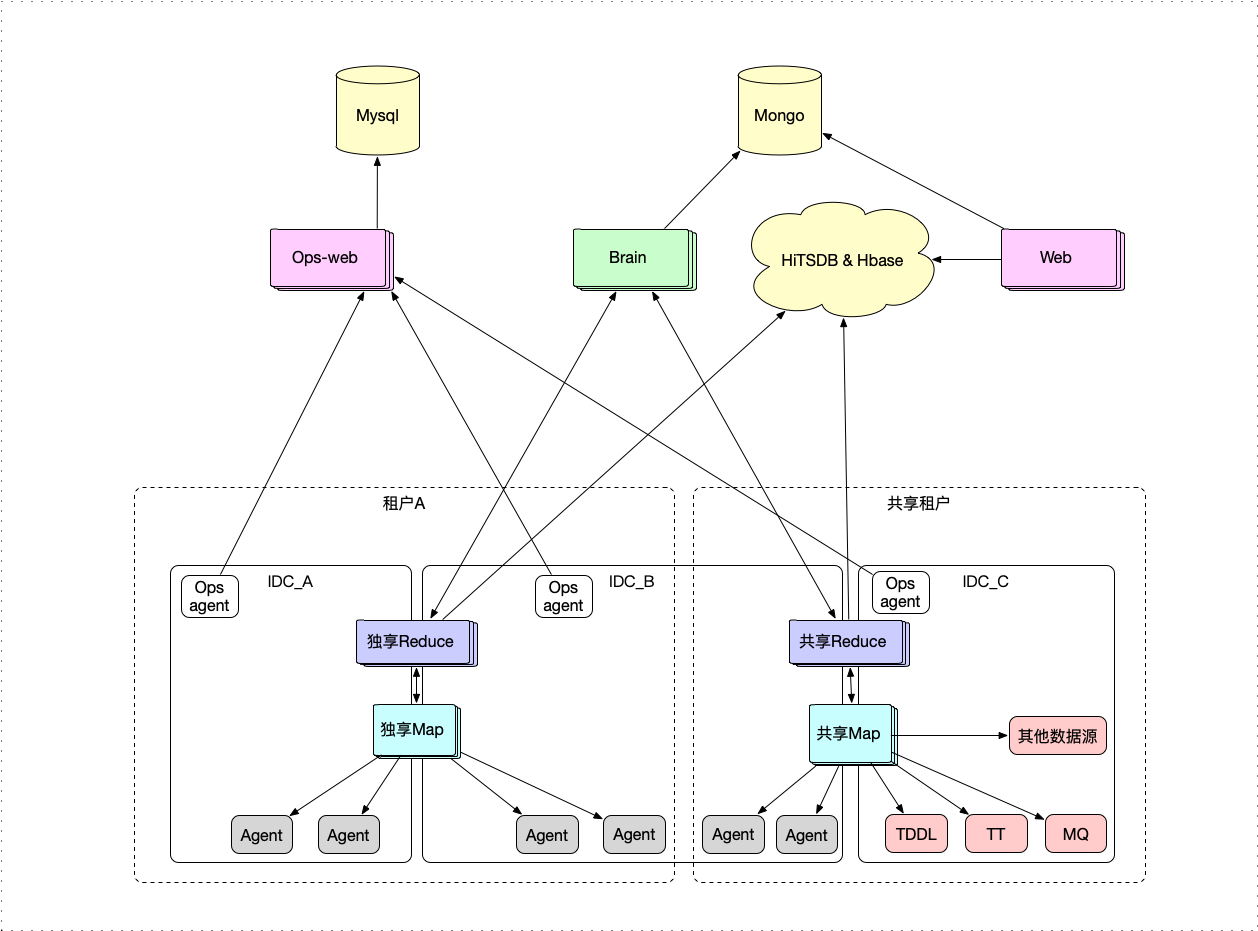
背景
公司内部的一个业务监控系统(上图是部署结构),目前主要的数据源就是日志.所以在日志采集方面,做了很多优化,今天就来说说Agent采集数据的一个小技巧.
问题
从上面的部署图中可以看到数据是通过部署在应用机器上的Agent来采集数据的.这就带来一个要求:Agent消耗的系统资源要非常低.绝对不能因为Agent导致应用自身出问题.我们的Agent是用Java写的,所以我们把最大堆内存设置为100MB.但很多应用的日志量都非常大,特别是在大促场景中,一分钟产生几个GB的日志是很正常的事情.在说解决方案之前,先来说说我们的原则.
原则
我们在实现Agent的时候,认为应用机器上的CPU和内存的都是比较宝贵的资源,Agent能不用就不用.所以我们在拉取日志的时候甚至都没做压缩.目的就是想用带宽换CPU和内存,带来的后果就是需要传输大量的原始日志数据.
解决方案
解决的方法也非常简单,就是利用了netty中的zero copy.为了简化代码,我写了一个比较简单的类.就是用netty启动一个http服务,访问/zero的时候就走zero copy的逻辑,其他路径就走普通逻辑.我用的测试文件test.log的大小为10MB.
Netty: 4.0.21.Final
JDK: 1.8.0_66
NettyHttpServer.java
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
| import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.Channel;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelOption;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpServerCodec;
public class NettyHttpServer {
static int PORT = 8080;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1);
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
ServerBootstrap server = new ServerBootstrap();
server.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 1024);
server.group(bossGroup, workerGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
public void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new HttpServerCodec());
ch.pipeline().addLast(new HttpServerInboundHandler());
}
});
server.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 1024);
server.childOption(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, true);
server.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, false);
Channel ch = server.bind(PORT).sync().channel();
System.out.println("server started");
ch.closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
|
HttpServerInboundHandler.java
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
| import java.io.File;
import java.io.RandomAccessFile;
import org.apache.commons.io.FileUtils;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter;
import io.netty.channel.DefaultFileRegion;
import io.netty.channel.FileRegion;
import io.netty.handler.codec.http.DefaultFullHttpResponse;
import io.netty.handler.codec.http.DefaultHttpResponse;
import io.netty.handler.codec.http.FullHttpResponse;
import io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpHeaders;
import io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpRequest;
import io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpResponse;
import io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpResponseStatus;
import io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpVersion;
import io.netty.handler.codec.http.LastHttpContent;
public class HttpServerInboundHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
private static Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(HttpServerInboundHandler.class);
private static String FILE_PATH;
static {
String homePath = System.getProperty("user.home");
FILE_PATH = homePath + "/test/test.log";
}
@Override
public void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) {
}
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
if (msg instanceof HttpRequest) {
HttpRequest req = (HttpRequest)msg;
String url = req.getUri();
try {
if (url.equals("/zero")) {
final RandomAccessFile raf = new RandomAccessFile(FILE_PATH, "r");
final FileRegion region = new DefaultFileRegion(raf.getChannel(), 0, raf.length());
HttpResponse response = new DefaultHttpResponse(HttpVersion.HTTP_1_1, HttpResponseStatus.OK);
response.headers().set(HttpHeaders.Names.CONTENT_TYPE, "text/plain");
response.headers().set(HttpHeaders.Names.CONTENT_LENGTH, raf.length());
ctx.write(response);
ctx.write(region);
ctx.writeAndFlush(LastHttpContent.EMPTY_LAST_CONTENT);
logger.info("zero copy");
} else {
byte[] targetFile = FileUtils.readFileToByteArray(new File(FILE_PATH));
FullHttpResponse response = new DefaultFullHttpResponse(HttpVersion.HTTP_1_1,
HttpResponseStatus.OK, Unpooled.wrappedBuffer(targetFile));
response.headers().set(HttpHeaders.Names.CONTENT_TYPE, "text/plain");
response.headers().set(HttpHeaders.Names.CONTENT_LENGTH, targetFile.length);
ctx.writeAndFlush(response);
logger.info("normal");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error(e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) {
logger.error(cause.getMessage(), cause);
ctx.close();
}
}
|
验证
启动
1
| java -Xmx100m -Xms100m -jar mynetty.jar
|
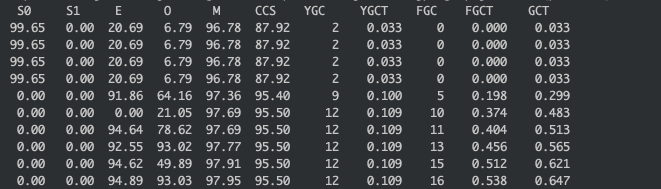
用jmeter开10线程去请求,普通写法的效果:
使用了zero copy的效果:
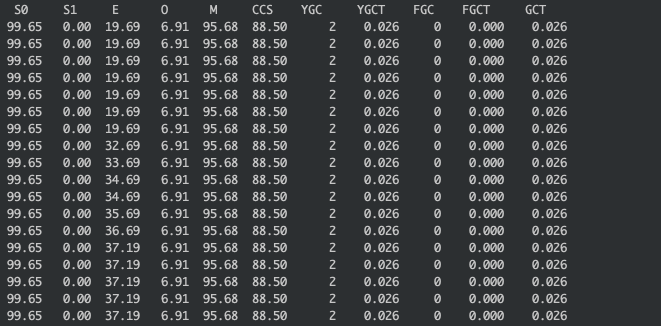
可以看到使用了zero copy的效果还是很明显的,没有产生任何的fullgc.
附录
通过零拷贝实现有效数据传输 英文版
对于Netty ByteBuf的零拷贝的理解


